Note: I wrote this article due to recent MyCERT announcement on this strain of ransomware. For some reason the MyCERT website has been unreliable and I noticed that it is a copy/paste of the FBI report, so i'm taking a stab at it here. Good news - the IOC is now copy/paste-able!
Introduction
As the cyber threat landscape continues to evolve, ransomware attacks remain a significant challenge for organizations worldwide. One such ransomware strain that has gained attention is the BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware. Recently, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) published an in-depth analysis of this ransomware and its activities[1]. In this article, we will delve into the technical details of BlackCat/ALPHV, its operators, and the Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) listed in the report. By understanding the characteristics and tactics of this ransomware, organizations can better prepare themselves to mitigate the risks associated with it.
BlackCat/APLHV Ransomware: A Closer Look
The BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware first emerged in 2021 and has since targeted organizations across various sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, and critical infrastructure[1]. It employs a double extortion model, which involves encrypting the victim's data and threatening to release sensitive information publicly if the ransom is not paid. This ransomware strain is known for its high level of sophistication and persistence in its attack campaigns.
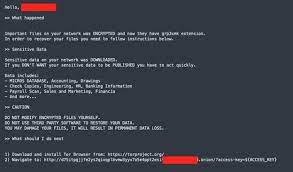
The operators behind BlackCat/ALPHV have demonstrated a high level of technical expertise, using advanced techniques to compromise networks, evade detection, and maintain persistence. They often use spear-phishing emails, malicious attachments, and remote desktop protocol (RDP) exploits to gain initial access to their targets' networks[1]. Once inside, they move laterally across the network, deploy additional malware, and exfiltrate sensitive data before initiating the encryption process.
Key Characteristics and Tactics of BlackCat/ALPHV
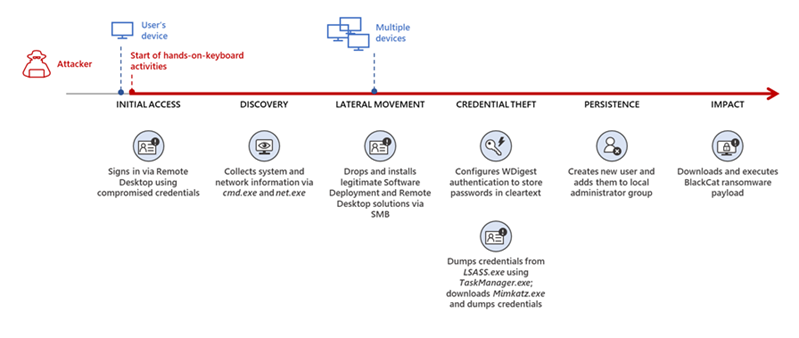
- Initial access: The BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware operators often use spear-phishing emails with malicious attachments, such as Microsoft Office documents containing macros, to compromise their targets[1]. They also exploit unsecured RDP connections to gain access to victim networks.It is also observed that the group uses stolen credentials to get initial access.
- Lateral movement: After gaining initial access, the operators move laterally across the network, often using living-off-the-land techniques and tools like Cobalt Strike[1]. They may also use custom tools and malware to maintain persistence and evade detection. The group has recently been seen compromising Active Directory Users and administrators accounts. Once compromised, the group uses Scheduled Tasks and Group Policy Objects to deploy the ransomware. Initial deployment uses Powershell scripts and also disables victim's network security. Tools such as Microsoft Windows administrative tools and SysInternals live were extensively used during compromise.
- Data exfiltration: Before encrypting the victim's data, the operators exfiltrate sensitive information, which they use as leverage in their extortion attempts[1]. They often use file transfer tools like FileZilla and WinSCP to transfer the stolen data to their command and control (C2) servers.
- Encryption and ransom demand: The BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware uses strong encryption algorithms to lock the victim's data, making it inaccessible without the decryption key[1]. The attackers then present a ransom demand, threatening to release the exfiltrated data publicly if the ransom is not paid within a specified timeframe.
- Persistence and evasion: The operators behind BlackCat/ALPHV have demonstrated a high level of persistence in their attack campaigns. They use a variety of techniques to maintain access to the compromised networks and evade detection, such as disabling security tools, clearing logs, and using process hollowing[1].
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
The FBI's report on the BlackCat/APLHV ransomware includes a list of IOCs associated with this threat. Organizations can use these IOCs to help identify potential compromises within their networks. Below is a copy/paste-able format of the IOCs provided in the report:
IP addresses:
- 89.44.9.243
- 142.234.157.246
- 45.134.20.66
- 185.220.102.253
- 37.120.238.58
- 152.89.247.207
- 198.144.121.93
- 89.163.252.230
- 45.153.160.140
- 23.106.223.97
- 139.60.161.161
- 146.0.77.15
- 94.232.41.155
Files:
- Powershell Scripts - MD5 Hash
- amd - Copy.ps1 861738dd15eb7fb50568f0e39a69e107
- ipscan.ps1 9f60dd752e7692a2f5c758de4eab3e6f
- Run1.ps1 09bc47d7bc5e40d40d9729cec5e39d73
- Batch Scripts: Filename - MD5 Hash
- CheckVuln.bat - f5ef5142f044b94ac5010fd883c09aa7
- Create-share-RunAsAdmin.bat - 84e3b5fe3863d25bb72e25b10760e861
- LPE-Exploit-RunAsUser.bat - 9f2309285e8a8471fce7330fcade8619
- RCE-Exploit-RunAsUser.bat - 6c6c46bdac6713c94debbd454d34efd9
- est.bat - e7ee8ea6fb7530d1d904cdb2d9745899
- runav.bat - 815bb1b0c5f0f35f064c55a1b640fca5
Executable and DLL: Filename - MD5 Hash
- http_x64.exe 6c2874169fdfb30846fe7ffe34635bdb
- spider.dll 20855475d20d252dda21287264a6d860
- spider_32.dll 82db4c04f5dcda3bfcd75357adf98228
- powershell.dll fcf3a6eeb9f836315954dae03459716d
- rpcdump.exe 91625f7f5d590534949ebe08cc728380
- Executable and DLL: Filename - SHA1 Hash
- mimikatz.exe d241df7b9d2ec0b8194751cd5ce153e27cc40fa4
- run.exe 4831c1b113df21360ef68c450b5fca278d08fae2
- zakrep_plink.exe fce13da5592e9e120777d82d27e06ed2b44918cf
- beacon.exe 3f85f03d33b9fe25bcfac611182da4ab7f06a442
- win1999.exe 37178dfaccbc371a04133d26a55127cf4d4382f8
- [compromised company].exe 1b2a30776df64fbd7299bd588e21573891dcecbe
Additional Filenames
- test.exe
- xxx.exe
- Mim.exe
- xxxw.exe
- crackmapexec.exe
- Services.exe
- plink.exe
- Systems.exe
- PsExec64.exe
- [###].ps1
- CME.ps1
- [#].ps1
- Run1.ps1
- mim.ps1
- [##].ps1
- psexec.ps1
- Systems.ps1
- System.ps1
BlackCat Ransomware SHA256 hash
- 731adcf2d7fb61a8335e23dbee2436249e5d5753977ec465754c6b699e9bf161
- f837f1cd60e9941aa60f7be50a8f2aaaac380f560db8ee001408f35c1b7a97cb
- 731adcf2d7fb61a8335e23dbee2436249e5d5753977ec465754c6b699e9bf161
- 80dd44226f60ba5403745ba9d18490eb8ca12dbc9be0a317dd2b692ec041da28
Recent Developments
Its no secret that the manufacturing industry was hit by this ransomware. Just yesterday, ALPHV group released the following statement.

Western Digital manufactures hard drive, and they have a plant in Bayan Lepas, Penang, Malaysia. I was told that the plant was also affected by this ransomware. This may explain the sudden release of the advisory by MyCERT. APLHV claims that Western Digital filed the Form 8-K with SEC with misleading information. Very strong words from the ransomware group indeed!
Reference:
[1] Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). (2022). BlackCat/ALPHV Ransomware. Retrieved from https://www.ic3.gov/Media/News/2022/220420.pdf
Conclusion
The BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware presents a significant threat to organizations across various sectors. Its operators are highly skilled and persistent in their attack campaigns, using sophisticated techniques to compromise networks, evade detection, and maintain persistence. By understanding the tactics and characteristics of this ransomware strain, organizations can better prepare themselves to mitigate the risks associated with it.
It is crucial for businesses to implement robust cybersecurity measures, such as regular patching, employee training, and network segmentation, to protect themselves from the growing threat of ransomware. Additionally, organizations should maintain up-to-date backups of their critical data, enabling them to recover from a ransomware attack without having to pay the ransom.
As the cyber threat landscape continues to evolve, organizations must remain vigilant and adapt their cybersecurity strategies to counter emerging threats like the BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware. By staying informed and proactive in their cybersecurity efforts, businesses can minimize the impact of ransomware attacks and protect their valuable data and resources.