Navigating the Storm: The OCBC Phishing Scandal and Its Aftermath
Introduction
The OCBC phishing scandal, unfolding over several months in 2023, has become a landmark case in the realm of cybersecurity within the financial sector. This case study offers an in-depth exploration of the events, the responses, and the lasting impacts on the industry.
Timeline of Events
Terse Timeline
• December 2021 - OCBC Customer started receiving SMS phishing messages, suposedly from the bank.
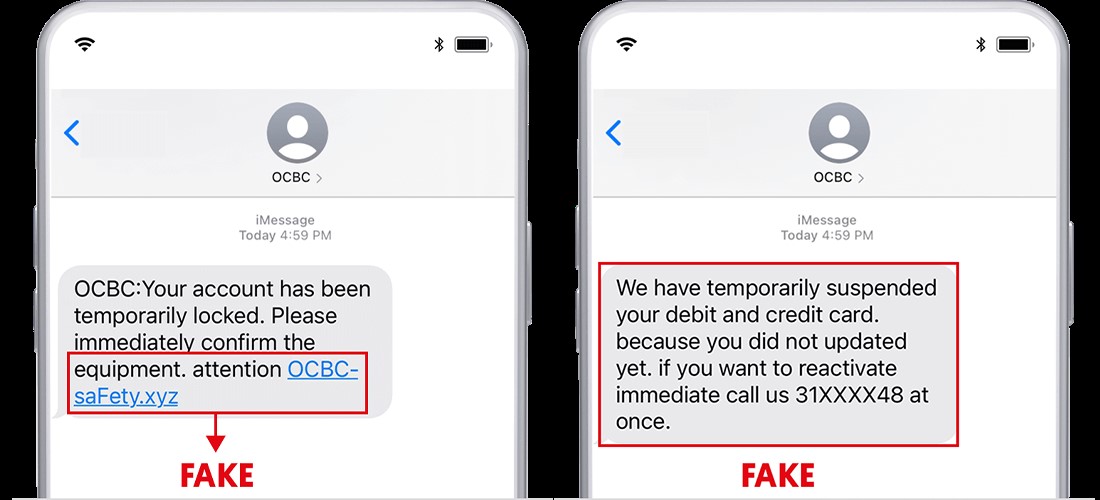
• 31 December 2021, OCBC implemented a 24-hour cooling off period for digital token provisioning. This was later revised to 12 hours, to align with the MAS and ABS industry measures.
• 1 January 2022, OCBC joined the IMDA Singapore SMS Anti-Spoofing Registry to have the Bank’s registered SMS sender IDs protected.
• 11 January 2022, OCBC have removed clickable links in all marketing emails and SMSes. Links were never embedded in SMSes on banking transactions prior to the scam.
• 14 January 2022, OCBC had reduced the default funds transfer daily limit for PayNow, and customers are now able to adjust it to their needs. The amount allowed to be transferred per transaction was also reduced. Transaction notifications for PayNow and FAST transfers are at S$0.01.
• 18 January 2022, the dedicated customer service care team set up in December 2021 to handle customer queries and reports on fraud has been made permanent. OCBC hotline (1800 363 3333) now contains a dedicated option “9” for customers to escalate reports of suspected scams.
• 19 January 2022 – the day which MAS and ABS announced the industry measures to bolster the security of digital banking – OCBC had already implemented most of the measures.
• On 31 January 2022 - OCBC implemented a cooling off period of at least 12 hours for key account changes such as updating a customer’s mobile number for notifications, to align with the industry measures.
• 16 February 2022 - OCBC have introduced a “kill switch” solution at all OCBC ATMs and via official OCBC contact number to enable customers to immediately freeze all their current and savings accounts in an emergency.
• June 2022 - OCBC deploy a team onsite at the Singapore Police Anti-Scam Centre to further enhance the speed of recovering monies stolen through scams.
Initial Phishing Attacks
The first signs of the phishing attacks emerged in December 2021, targeting OCBC customers with sophisticated social engineering tactics. This section details the nature of these attacks, the vulnerabilities exploited, and the initial impact on customers and the bank.
In December 2021, OCBC customers became the targets of a sophisticated phishing campaign, marking the beginning of a significant cybersecurity incident. These attacks were not just technologically advanced but also psychologically manipulative, leveraging the trust and urgency typically associated with bank communications. The fraudsters meticulously crafted emails and SMS messages that appeared to be from OCBC, complete with official logos and language. These communications often contained alarming messages about security breaches or account verification requirements, urging customers to take immediate action. The links provided in these messages redirected unsuspecting customers to counterfeit websites, expertly designed to mimic OCBC's legitimate online portals.
OCBC's Response (December 2021): In response to the phishing attacks that began in December 2021, OCBC took several immediate and strategic steps to mitigate the damage and address the concerns of its customers and the public. The bank's response was multifaceted, focusing on customer support, security enhancement, and transparent communication.
As soon as the phishing attacks were identified, OCBC swiftly initiated a crisis response protocol. Around [specific date], they set up a dedicated helpline and support system for affected customers. This move was crucial in providing immediate assistance to those who had fallen victim to the scam, helping them secure their accounts and begin the process of recovering lost funds. OCBC also launched an extensive information campaign, both online and offline, to educate its customers about the phishing scam. This campaign, which started around [specific date], aimed to raise awareness about the nature of the attacks and how to identify and avoid similar scams in the future.
Regulatory Intervention by MAS (Date/Month 2023): The Monetary Authority of Singapore's intervention was a turning point in the incident. This section delves into MAS's investigative process, the directives issued to OCBC, and the broader regulatory implications, highlighting the actions taken and their effectiveness. Industry-Wide Impact (Date/Month 2023): The repercussions of the OCBC phishing scandal were felt across the entire financial sector. This section assesses the broader implications for cybersecurity in banking, including the heightened focus on digital security and the ripple effects on other financial institutions. Analysis of MAS's Response:
Regulatory Measures (Date/Month 2023): MAS's response included a range of measures aimed at enhancing cybersecurity resilience. This section provides a detailed examination of these measures, evaluating their strategic value and potential for shaping future cybersecurity policies in the financial sector. Critical Review (Date/Month 2023): Offering a balanced critique of MAS's actions, this section considers the adequacy, timeliness, and long-term implications of their response, weighing the benefits against potential drawbacks. Industry Feedback and Recommendations:
Feedback from Financial Institutions (Date/Month 2023): This section presents a diverse range of opinions and reactions from various stakeholders within the industry, providing a multifaceted view of the incident's impact. Recommendations for Future Prevention (Date/Month 2023): Concluding with actionable strategies, this section emphasizes the importance of advanced cybersecurity practices, customer awareness, and regulatory vigilance, proposing robust measures for enhancing cybersecurity resilience in the financial sector. Conclusion: The OCBC phishing scandal serves as a crucial learning point for the financial industry. This section summarizes the key takeaways, stressing the need for proactive security measures and the critical role of regulatory bodies in ensuring a secure and resilient financial ecosystem.
References:
[1] OCBC Media. Retrieved from https://www.ocbc.com/group/media/release/2022/media-statement-mas-response.page