Introduction: The Evolving Threat Landscape and the Need for Structured Response
In today's increasingly interconnected world, data breaches are no longer a question of "if," but "when." With the exponential growth of digital information and the ever-evolving tactics of cybercriminals, organizations of all sizes face a constant threat of having their sensitive data compromised. A single incident can result in the loss of millions of dollars, damage to brand reputation, and regulatory penalties, highlighting the critical need for a well-defined and effective response strategy.
While preventing a data breach altogether should always be the primary goal, the reality is that even the most robust security measures can be breached. This is where a robust incident response plan becomes essential. It serves as a roadmap for organizations to navigate the complex and often chaotic aftermath of a data breach, minimizing the impact and enabling a swift recovery.
This article delves into the world of data breach incident response, specifically focusing on the framework and guidance offered by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). By drawing upon internationally recognized standards like ISO/IEC 27001:2013 and ISO/IEC 27035:2021, we will explore the vital stages of incident response, from preparation and detection to containment, recovery, and improvement. We will also delve into data breach-specific considerations such as notification requirements, forensic investigation, and public relations management.
By the end of this article, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to implement an ISO-based data breach response plan, equipping your organization with the tools and knowledge necessary to effectively manage and mitigate the impact of a data breach.
Understanding Data Breaches What is a Data Breach?
According to ISO/IEC 27035:2021, a data breach is "a security incident that results in the unauthorized disclosure, access, acquisition, alteration, or destruction of personal data, or the unauthorized access to, or use of, operational data" (Clause 3.3). In simpler terms, it occurs when sensitive information is accessed or stolen by someone who is not authorized to do so.
Data breaches can involve a variety of types of information, including:
Personally identifiable information (PII): This includes names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, Social Security numbers, financial information, and medical records. Operational data: This includes information that is essential for the operation of an organization, such as trade secrets, intellectual property, and customer data.
Types of Data Breaches
Data breaches can occur in a variety of ways, and the specific method used can have a significant impact on the severity of the incident. Some of the most common types of data breaches include:
- Hacking: This is when attackers gain unauthorized access to computer systems and networks, often through phishing emails, malware, or social engineering attacks.
- Physical theft: This can occur when laptops, hard drives, or other devices containing sensitive data are lost or stolen.
- Insider threats: This is when employees or contractors who have authorized access to data misuse their privileges and steal or leak information.
- Cloud breaches: This can occur when data stored in the cloud is compromised due to vulnerabilities in the cloud provider's infrastructure or security controls.
Impact of Data Breaches
Data breaches can have a devastating impact on organizations, both financially and reputationally. Some of the potential consequences include:
Financial losses: Organizations can face significant financial losses due to fines, legal settlements, data recovery costs, and lost business. Reputational damage: Data breaches can erode consumer trust and damage an organization's reputation, leading to decreased sales and customer loyalty. Regulatory penalties: Organizations that violate data privacy regulations can face hefty fines and other penalties. The Importance of Protecting PII
In today's digital age, personally identifiable information (PII) has become an increasingly valuable commodity. PII can be used for a variety of malicious purposes, including identity theft, fraud, and discrimination. As a result, organizations have a heightened responsibility to protect PII and ensure that it is handled securely.
In the next section of this article, we will explore the ISO-based framework for incident response, providing a structured approach to preparing for, detecting, and responding to data breaches.
ISO-Based Incident Response Framework: A Structured Approach to Data Breach Response
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed a comprehensive framework for information security management, including incident response. This framework, outlined in ISO/IEC 27001:2013 and further detailed in ISO/IEC 27035:2021, provides a standardized and structured approach to data breach response, allowing organizations to effectively manage and mitigate the impact of such incidents.
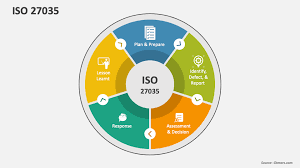
The ISO-based incident response framework consists of five key stages:
1. Preparation and Prevention:
This stage focuses on establishing the necessary groundwork to prevent data breaches and ensure a swift response if one occurs. Key activities include:
Risk assessments: Identifying and analyzing potential threats and vulnerabilities related to data security. Vulnerability management: Implementing a program to identify and patch vulnerabilities in systems and applications.
Security awareness training: Educating employees and contractors on cyber security best practices and how to identify and report suspicious activity. Incident response plan development: Creating a documented plan that outlines roles, responsibilities, communication protocols, and response procedures for different types of incidents. Testing and exercises: Regularly testing and updating the incident response plan through drills and simulations.
2. Detection and Reporting:
This stage involves identifying and reporting potential data breaches as soon as possible. Key activities include:
- Monitoring security events: Implementing security tools and processes to monitor systems and networks for suspicious activity.
- Log analysis: Reviewing system logs and other data sources to identify potential indicators of compromise.
- User reporting: Establishing clear procedures for employees and stakeholders to report suspected data breaches.
- Threat intelligence: Utilizing threat intelligence feeds and other resources to stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
3. Containment and Eradication:
This stage focuses on containing the damage from a data breach and preventing further harm. Key activities include:
Isolating affected systems: Disconnecting compromised systems from the network to prevent the spread of malware or unauthorized access. Identifying root causes: Determining the cause of the data breach and how the attacker gained access to the system. Eradicating the threat: Removing malware or other malicious tools from affected systems and preventing the attacker from regaining access.
4. Recovery and Restoration:
This stage focuses on restoring affected systems and data to a known clean state.
Key activities include:
- Data restoration: Restoring lost or damaged data from backups.
- System recovery: Rebuilding affected systems and ensuring their security is restored.
- Patching vulnerabilities: Patching any vulnerabilities that were exploited during the data breach.
5. Lessons Learned and Improvement:
This stage focuses on learning from the incident and improving the incident response plan for future events. Key activities include:
- Incident review: Conducting a thorough review of the incident to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement.
- Updating the incident response plan: Incorporating lessons learned and best practices into the incident response plan.
- Sharing information: Sharing information about the incident with other organizations to inform their own cyber security efforts.
By following the ISO-based incident response framework, organizations can develop a comprehensive and effective approach to data breach response. This framework provides a structured roadmap for navigating the complex aftermath of a data breach, minimizing the impact on the organization and its stakeholders.
In the next section, we will delve into the additional considerations specific to data breach response, such as notification requirements, forensic investigations, and public relations management.
Data Breach Specific Considerations: Tailoring the Response Plan
While the ISO-based framework provides a solid foundation for incident response, data breaches often necessitate additional considerations beyond the general approach. This section explores several key aspects specific to data breach response:
1. Data Breach Notification:
Following a data breach, prompt notification of affected individuals and relevant authorities is crucial. Notification requirements vary depending on the location and type of data involved. Organizations must be familiar with applicable data privacy regulations such as:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union: Requires notification to the supervisory authority within 72 hours if the breach is likely to result in a high risk to individuals. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States: Requires notification to affected residents without unreasonable delay.
Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) in Canada: Requires notification to the Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada and affected individuals if the breach poses a real risk of significant harm.
Organizations should also consider notifying the media and other stakeholders depending on the severity of the breach and the potential impact on their reputation.
2. Forensic Investigation:
Conducting a thorough forensic investigation is vital to determine the scope of the breach, identify the root cause, and gather evidence for potential legal action. A skilled forensic investigator can help:
- Analyze logs and other data to reconstruct the timeline of the attack.
- Identify the methods used by the attackers.
- Find the source of the breach and any vulnerabilities that were exploited.
- Collect and preserve evidence for law enforcement or legal proceedings.
3. Public Relations and Reputation Management:
Effective communication with stakeholders, including customers, employees, and the media, is critical during and after a data breach. Organizations should develop a clear and consistent communication strategy to:
- Acknowledge the breach publicly and express regret for any inconvenience caused.
- Provide accurate and timely information about the nature and scope of the breach.
- Explain the steps being taken to contain the damage and protect affected individuals.
- Offer resources and support to impacted individuals, such as credit monitoring or identity theft protection.
- Address concerns and answer questions from stakeholders transparently.
By implementing a well-defined public relations and reputation management strategy, organizations can minimize the damage to their reputation and regain the trust of their stakeholders.
4. Regulatory Compliance:
Failure to comply with data breach notification requirements can lead to significant fines and penalties. Organizations should ensure their data breach response plan adheres to all applicable data privacy regulations to avoid legal repercussions.
By incorporating these data breach-specific considerations into their incident response plan, organizations can ensure a comprehensive and effective response that minimizes the impact of a data breach and protects the sensitive information entrusted to them.
Implementing an ISO-Based Data Breach Response Plan: Building a Strong Defense
Now that we have examined the theoretical framework and crucial considerations for data breach response, let's delve into the practical aspects of implementation. Building a robust data breach response plan based on ISO standards offers organizations a structured and efficient approach to mitigating potential risks.
1. Establish a Dedicated Incident Response Team:
Assemble a team of individuals with expertise in security, IT, legal, and public relations to manage the incident response process effectively. Delegate clear roles and responsibilities for each team member to ensure swift and coordinated action.
2. Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities:
Outline the specific roles and responsibilities of each team member for various stages of the incident response process. This clarity fosters accountability and ensures that everyone knows their part in mitigating the breach.
3. Develop and Document Response Procedures:
Document detailed procedures for each stage of the incident response process, outlining the steps to be taken, tools to be utilized, and communication protocols to be followed. This documentation ensures consistency and provides a roadmap for team members during a crisis.
4. Conduct Regular Training and Drills:
Regularly train your incident response team on the established procedures and best practices for data breach response. Implement drills and simulations to test their knowledge, identify gaps in the response plan, and refine their skills in a controlled environment.
5. Maintain and Update the Plan Regularly:
Data breaches and cyber threats constantly evolve, necessitating regular updates and revisions to the incident response plan. Keep abreast of emerging threats, adapt the plan to address new vulnerabilities, and incorporate lessons learned from past incidents.
6. Leverage Technology:
Automate routine tasks such as log analysis and vulnerability scanning to free up team members for more critical activities. Utilize incident response tools and platforms to streamline communication, reporting, and data recovery processes.
7. Foster a Culture of Security:
Building a culture of security within the organization is crucial to preventing data breaches. Promote awareness among employees regarding cyber threats and best practices for data security. Encourage reporting of suspicious activity and empower individuals to contribute to a secure environment.
8. Continuously Monitor and Improve:
Regularly monitor and assess the effectiveness of your incident response plan. Evaluate its strengths and weaknesses, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to strengthen your overall data breach response capabilities.
By adhering to these implementation steps, organizations can effectively leverage the ISO-based framework to construct a robust and dynamic data breach response plan. This plan will serve as a vital tool for mitigating potential risks, ensuring business continuity, and protecting sensitive information in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
Conclusion
Data breaches pose a significant threat to organizations of all sizes, demanding a proactive and comprehensive approach to incident response. By adopting the ISO-based framework and incorporating the data breach-specific considerations outlined in this article, organizations can create a structured and effective response plan that minimizes the impact of an incident and protects their critical assets. By fostering a robust security culture, investing in technology, and continuously monitoring and improving their response capabilities, organizations can build resilience and ensure their long-term success in the face of evolving cyber threats.
References
[1] ISO/IEC 27001:2013 Information technology – Security techniques – Information security management systems – Requirements [2] ISO/IEC 27035:2021 Information technology – Security techniques – Information security incident management [3] National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework [4] General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)